Coronary Angioplasty
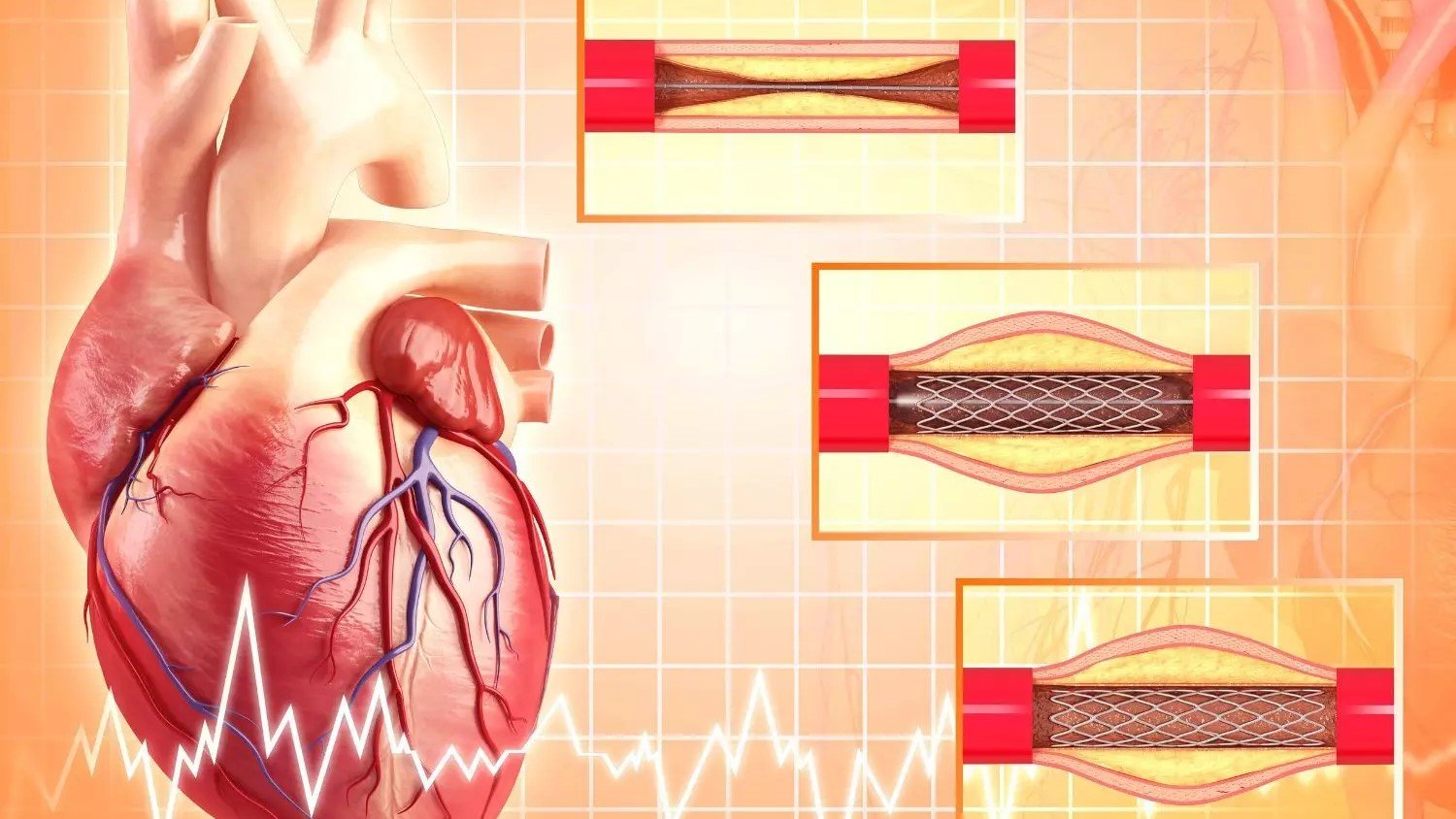
Procedure of Angioplasty
The Coronary Angioplasty procedure done in various process:
Access:
Access artery, insert catheter in groin/wrist, apply anesthetic for comfort. Treats blockages/narrowing in arteries.
Imaging and Evaluation:
A contrast dye is injected through the catheter, and X-ray imaging is used to visualize the coronary arteries. This helps the cardiologist identify the location and severity of the blockage.
Balloon Inflation:
Balloon-tipped catheter advances to blockage, inflates, widening artery, restoring blood flow by pressing plaque against walls.
Stent Placement (if necessary):
Stent inserted after balloon inflation keeps the artery open, a wire mesh tube locks in place and pushes plaque.
Recovery:
Angioplasty’s crucial aspect is recovery, monitoring the patient’s ability to resume daily activities. Cardiac rehab can aid healing.
Why It’s Done ?
Benefits
1. Minimally invasive procedure with smaller incisions and reduced recovery time.
2. Immediate relief from angina symptoms and reduces the risk of heart attack by opening blocked arteries and preventing blood clots.
3. Long-term benefits, including stabilization of coronary artery disease and potential life expectancy improvement.
Risks Involved
Types of Angioplasty
There are also other several types of angioplasty test procedures based on the targeted vessels:
Peripheral Angioplasty
Treats narrowed arteries in the legs, arms, and other peripheral areas.
Carotid Angioplasty
Addresses stenosis in the carotid arteries, reducing the risk of stroke.
Renal Angioplasty
Dilates narrowed arteries in the kidneys to improve kidney function.
Balloon Angioplasty
Utilizes a balloon catheter to widen the narrowed artery.
What is done after the procedure of Angioplasty?
All patients are carefully followed after angioplasties for any complications. The use of medicinal products to treat the pain and avoid blood clots is recommended. Care instructions, including wound care, medication management and lifestyle changes are given to patients after the angioplasty process. Follow-up appointments are scheduled to assess progress and ensure ongoing care.
In Nagpur, coronary angioplasty is a widely available and advanced medical procedure used to treat blocked coronary arteries. Skilled cardiologists perform the minimally invasive technique, which involves inserting a balloon or stent to open narrowed arteries, restoring blood flow to the heart, and improving patients’ cardiac health. And the Coronary Angioplasty cost in Nagpur is very efficient. Dr. Chetan Rathi is one of the Heart Specialists who perform Coronary Angioplasty in Nagpur.
FAQ's for Coronary Angioplasty Procedure in Nagpur
What is angioplasty surgery?
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the use of catheters with small balloons to widen vessels and improve blood flow into the heart for narrowing or blocked arteries.
